
The porous sprayed surface has microscopic contoured troughs and ridges. The femoral component is usually covered with a porous surface on the upper end. Uncemented hip replacement uses specially designed prosthetic components for the bone to implant fixation. The cement mantle ensures adequate fixation in patients with a wide femur (Dorr C).

The porous bones may not support the uncemented implant due to poor bone ingrowth. Osteopenic or osteoporotic patients have thin and porous bones.The cemented hip replacements are indicated only in limited cases: Beads may be used at the cement implant prosthesis to ensure an even cement distribution and to prevent bottoming out of the cement. The acetabulum cementing is rarely done but is similarly done to ensure adequate fixation.A proximal seal is made to ensure adequate pressure during the polymerization of the cement.

The femoral stem is inserted to pressurize the cement and the tapered stem design ensures the cement pressure is maintained during the insertion.The gun ensures the cement is not eviscerated by the bleeding in the canal. The cement is filled in the canal using a cement gun that pressurizes the cement injection in the canal.A cement restrictor is placed at an appropriate distance to prevent the cement from traveling down the canal.
HIP REPLACEMENT XRAY SERIAL
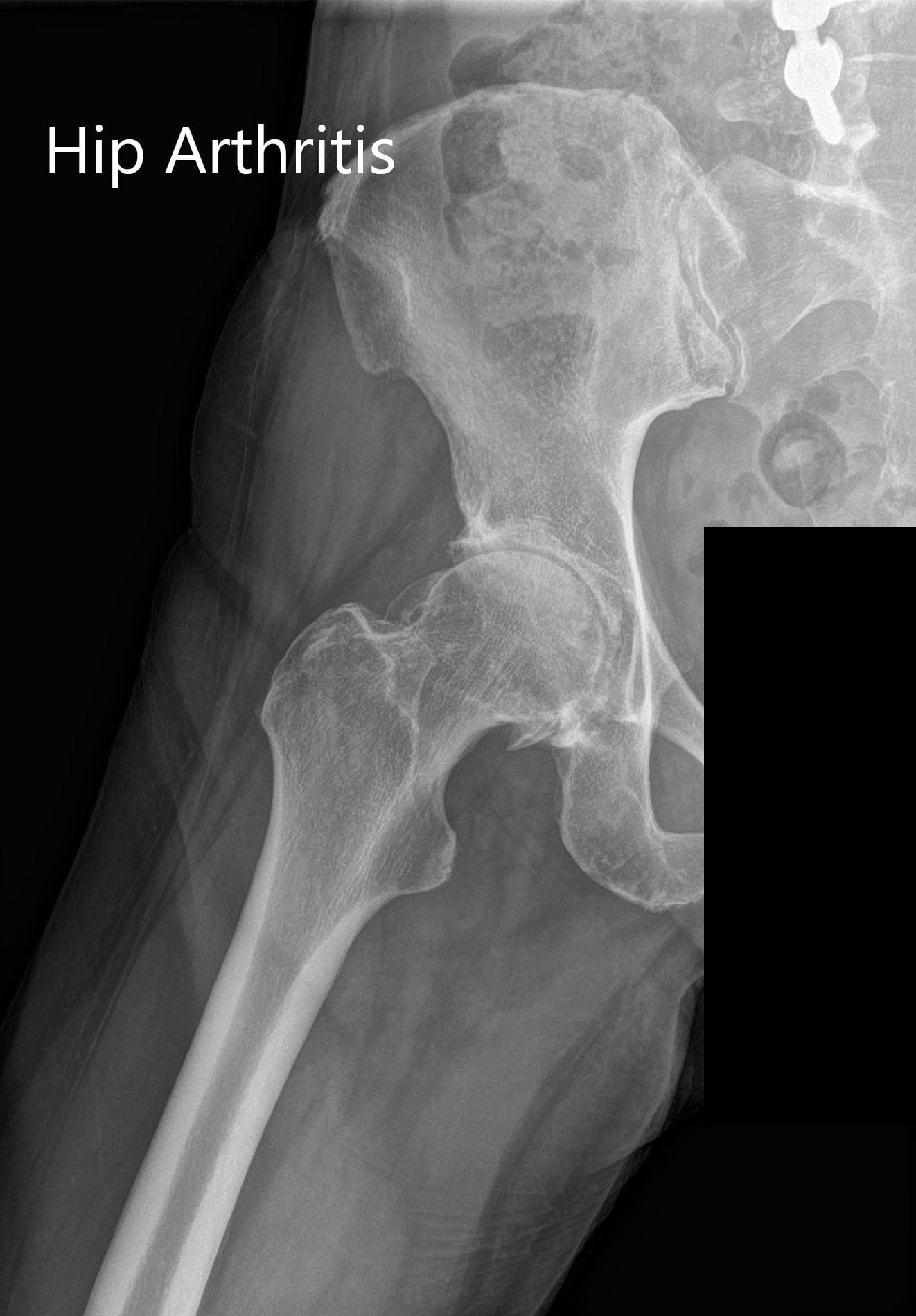
Preparation of the femoral canal using serial broaching and using a pulsatile lavage to wash the canal and remove debris.The modern technique of cementing involves: The bone cement hardens in about 10 minutes in the OR temperature. The modern mixing in the operating room involves the use of a vacuum mixer. The mixing and cementing techniques have evolved in the past decades to achieve maximum fixation. The bone cement is made by mixing powder and liquid components. The bone cement creates a grout and fixes the implant by acting as an interlocking surface between the implant and the bone rather than simply gluing the implant to the bone. Cemented Hip ReplacementĪ cemented hip replacement uses a polymethylmethacrylate (PMMA) bone cement to fix the implant surface to the bone. Uncemented hip replacements rely on bone on-growth over specially designed implants. A cemented hip arthroplasty relies on bone cement to fix the implants to the bone interface. X-ray of the hip in lateral view showing a partial cemented hip replacement.Ĭemented and uncemented hip arthroplasties differ in how the prosthetic implant is fixed to the natural bone.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
